The Great Debate: Sugar Beet Vs Sugar Cane - Which Is the Superior Choice for Sweeteners?
The debate over sugar beet versus sugar cane as the favored sugar involves a number of vital elements. Each deals distinct advantages and obstacles relating to manufacturing, taste, and health and wellness ramifications. While sugar beet may attract those focusing on sustainability, sugar cane has its very own social and cooking significance. As customers become more mindful of their selections, the concern stays: which sweetener really stands out in today's market?
The Origins of Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane
Although sugar cane has been cultivated for thousands of years, mainly in tropical areas, sugar beet became a substantial choice in cooler climates throughout the 18th century. Sugar cane, native to Southeast Asia, was first tamed around 8000 BCE and spread out around the world via trade and expedition. Its high sucrose content made it a valuable crop, leading to comprehensive vineyards in areas like the Caribbean and Brazil.
In comparison, sugar beet was first cultivated in the Mediterranean around the 18th century, especially gaining traction in Europe as a reaction to sugar cane shortages. The plant prospers in warm environments, making it appropriate for areas with cooler weather. The exploration that sugar might be extracted from beet origins changed sweetener production, especially during the Napoleonic Wars when trade limitations minimal cane sugar access. The rise of sugar beet growing noted a critical minute in the background of sweeteners, supplying a regional source for many countries.
Production Processes: From Area to Sugar
The manufacturing processes of sugar beet and sugar cane expose considerable differences in farming methods, collecting methods, and refinement stages. Understanding these nuances is necessary for valuing how each crop contributes to the overall sugar market. This contrast highlights the one-of-a-kind characteristics and challenges associated with both sources of sweetness.

Cultivation Strategies Comparison
Growing strategies for sugar beet and sugar cane disclose distinct approaches that influence their production procedures, from field preparation to final sweetener removal. Sugar beet cultivation usually entails plowing and harrowing to develop a fine seedbed, adhered to by seeding in rows to promote growth. This crop gain from cooler climates and is usually planted in spring. On the other hand, sugar cane is normally planted in furrows with pre-sprouted cane items, calling for a warm, tropical climate for optimal growth. Cane fields are commonly laid out to handle water efficiently, given its need for substantial watering. Both plants are taken care of with details fertilizing and insect control methods tailored to their growth atmospheres, impacting return quality and performance in sugar extraction.
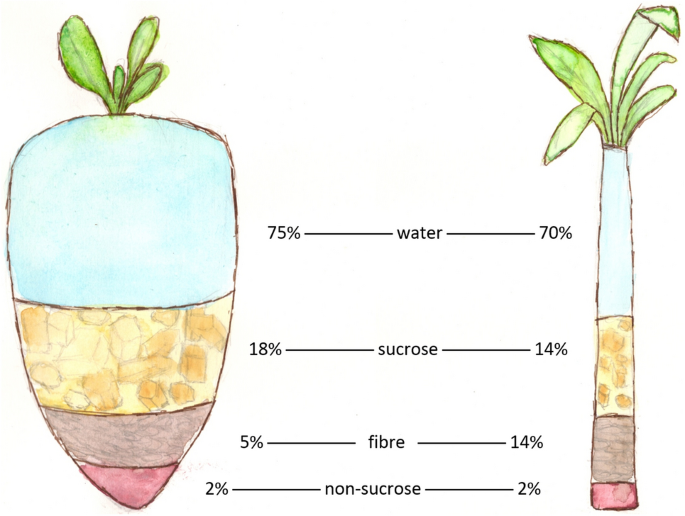
Gathering Approaches Described
Efficient collecting methods for sugar beet and sugar cane play a vital duty in guaranteeing maximum return and quality of the end product. Sugar beet gathering typically employs mechanized origin harvesters, which efficiently uproot the beetroots from the soil and separate them from the vegetation. This method reduces damage to the beets and decreases labor prices. In comparison, sugar cane harvesting might use either manual work or equipment, relying on the area and scale of manufacturing. Mechanical farmers cut the cane at the base and usually strip away the fallen leaves, optimizing the procedure for bigger fields. Both techniques need mindful timing to guarantee the crops are harvested at peak sweetness, affecting the high quality of the final sweetener item.
Improvement Process Distinctions
While both sugar beet and sugar cane undertake extensive refinement procedures to change their raw types right into usable sugar, the methods used vary substantially. Sugar beet improvement begins with washing and slicing the beetroots right into slim cossettes, adhered to by diffusion, where warm water essences sucrose. The resulting juice is then purified, concentrated, and crystallized. On the other hand, sugar cane processing entails crushing the stalks to remove juice, which is after that made clear utilizing lime and heat to remove contaminations. The cane juice is evaporated to create syrup prior to condensation. Ultimately, while both procedures aim to generate white sugar, the distinctive techniques highlight the special qualities of each source and their ramifications for taste and pureness in the last product.
Nutritional Profiles: What's in Your Sweetener?
The nutritional profiles of sugar beet and sugar cane present unique differences worth checking out. This comparison consists of aspects such as caloric web content, mineral and vitamin visibility, and variants in glycemic index. Understanding these variables can supply understandings right into just how each sugar may affect overall wellness.
Calorie Web Content Contrast
Comprehending the calorie web content of sugar beet and sugar cane is crucial for those conscious of their nutritional options. Both sweeteners primarily consist of sucrose, adding a similar caloric worth. Commonly, sugar beet consists of roughly 387 calories per 100 grams, while sugar cane has concerning 390 calories per the same quantity. The slight distinction in caloric material might not considerably influence most diet regimens; however, it is impressive for those carefully checking their caloric intake. Furthermore, both sugar resources supply power yet lack crucial nutrients, making them mainly sources of empty calories. People looking for much healthier choices might desire to take right into account these elements when selecting between sugar beet and sugar cane as their preferred sugar.
Mineral and Vitamin Material
Calorie web content supplies only a part of the image when assessing sugar beet and sugar cane. Both resources of sugar differ considerably in their mineral and vitamin accounts. Sugar beetroots are remarkably abundant in crucial nutrients, including potassium, magnesium, and iron. They also have percentages of vitamins such as B6 and folate, adding to their nutritional worth. In contrast, sugar cane provides a various collection of benefits, containing calcium, phosphorus, and traces of B vitamins. While neither choice is a significant source of minerals and vitamins view it contrasted to entire foods, sugar beets might have a small edge due to their greater mineral content. Ultimately, consumers seeking dietary gain from sweeteners must think about these distinctions in profiles.
Glycemic Index Distinctions
Glycemic index plays a necessary function in evaluating how different sweeteners influence blood sugar degrees. Sugar beet and sugar cane display remarkable differences in their glycemic actions. Typically, sugar beet has a lower glycemic index compared to sugar cane, causing a slower and steadier surge in blood glucose levels after intake. This characteristic may make sugar beet a better option for people managing diabetic issues or those seeking to preserve secure power degrees. In contrast, sugar cane tends to cause a more rapid spike in blood sugar, which could bring about quicker power accidents. Comprehending these differences is significant for customers aiming to make informed dietary options concerning sweeteners and their influence on overall wellness.
Ecological Influence: Sustainability Factors To Consider
While both sugar beet and sugar cane are essential sources of sugar, their ecological effects and sustainability considerations differ markedly. Sugar beets, primarily grown in temperate areas, typically need less water and can be grown in varied climates. They likewise take advantage of plant turning methods, which boost dirt wellness and lower the need for synthetic fertilizers. Intensive farming of sugar beets can lead to soil deficiency and chemical use.
In contrast, sugar cane flourishes in tropical environments and often demands substantial water sources for irrigation (Sugar beet vs sugar cane). The monoculture nature of sugar cane farming can intensify dirt disintegration and biodiversity loss. Furthermore, the burning of cane fields prior to harvest launches carbon discharges and adds to air contamination. Both crops deal with challenges related to environment adjustment, however their varying farming methods profoundly affect their general sustainability profiles. Therefore, the option between sugar beet and sugar cane entails weighing these environmental effects carefully
Preference and Culinary Makes Use Of: Which Sweetener Reigns Supreme?
The selection between sugar beet and sugar cane prolongs beyond environmental factors to consider to encompass preference and culinary applications. Sugar beet, frequently perceived as having a somewhat different flavor account, tends to be much less wonderful than sugar cane. This refined difference can influence its usage in dishes, especially in baked items where a neutral sweet taste is preferred.
On the other hand, sugar cane is commemorated for its distinctive, rich, and extra complicated taste, making it a preferred selection for drinks and desserts - Sugar beet vs sugar cane. Its natural molasses web content can enhance the depth of tastes in various meals
In food preparation, sugar cane's versatility shines via in marinades, lusters, and confections, while sugar beet is commonly discovered in refined foods and sugar like granulated sugar. Ultimately, the decision between the 2 sweeteners often depends upon private preference preferences and particular cooking applications, with each offering distinct benefits in the kitchen area.
Wellness Effects: Sugar Beet Vs Sugar Cane
Both sugar beet and sugar cane have unique health and wellness effects that can influence customer choices. Sugar beet vs sugar cane. Sugar beet is frequently related to for its greater fiber content, which can help digestive health. Additionally, it includes certain antioxidants that may add to general well-being. On the other hand, sugar cane is rich in nutrients such as calcium, potassium, and magnesium, providing some mineral advantages
Nonetheless, both sources mainly include sucrose, which can bring about similar health and wellness worries when consumed excessively, such as obesity, diabetes mellitus, and heart condition. The handling methods likewise vary; sugar beet is generally fine-tuned much more intensively, possibly leading to a loss of particular nutrients. Customers worried about ingredients might like sugar cane, as it commonly goes through much less processing. Ultimately, understanding these wellness implications can lead people toward making informed choices regarding their sweetener selections.
Customer Preferences: Trends and Insights
Consumer preferences for sweeteners have advanced significantly in the last few years, affected by wellness patterns, environmental issues, and nutritional options. Enhanced understanding of the unfavorable wellness results related to too much sugar intake has actually led many consumers to seek options. This change has actually triggered an expanding interest in all-natural sugar, with sugar beet and sugar cane going to the forefront of conversations.
Research study suggests that customers are significantly preferring sugar beet as a result of its perceived environmental benefits, as it is often expanded closer to refining plants, minimizing transport emissions. On the other hand, sugar cane is usually linked with exotic areas and may carry assumptions of sustainability challenges.

Frequently Asked Questions
Just How Do Sugar Beet and Sugar Cane Affect Blood Sugar Level Degrees?
Sugar beet and sugar cane both use this link contain sucrose, which can elevate blood sugar levels. The impact mostly relies on private metabolic process and usage amounts, however both resources contribute likewise to blood glucose reactions original site for the most part.
Which Sweetener Is Better for Cooking and Cooking?
When reviewing sweeteners for cooking and cooking, one have to think about texture, taste, and wetness retention. Sugar beet and sugar cane both supply one-of-a-kind top qualities, with sugar cane usually favored for its richer flavor profile in culinary applications.
Can Sugar Beet or Cane Be Made Use Of in Vegan Diets?
Both sugar beet and sugar cane can be made use of in vegan diet plans. They are plant-derived sugar, making them appropriate for people looking for vegan-friendly choices without animal items, guaranteeing ethical selections in their cooking techniques.
What Are the Historic Uses Sugar Beet and Cane?
Historically, sugar beet and cane served as vital resources of sweet taste, with cane cultivated in exotic areas and beet in warm zones. Both have actually been integral to different societies, economies, and culinary traditions throughout background.
Are There Any Kind Of Alternatives to Sugar Beet and Cane?
Alternatives to sugar beet and cane include agave nectar, honey, syrup, and man-made sweeteners like aspartame and sucralose. These substitutes use differing flavors and health and wellness advantages, appealing to varied nutritional preferences and restrictions.